Welcome, fellow construction specification enthusiasts! As you already know, maintaining the integrity of a building’s envelope is crucial to its performance, comfort, and longevity. One key aspect of a building’s envelope is its ability to protect against the elements — specifically, its thermal and moisture protection capabilities.

In this comprehensive guide, we will dive deep into the fascinating topic of CSI Division 07 — Thermal and Moisture Protection. This division is one of the most essential areas to master in construction specification, as it plays a critical role in the overall durability and energy efficiency of a building. My goal, as is to provide you with valuable content that will not only boost your understanding of thermal and moisture protection systems but also improve your ability to specify and implement them in your projects.
The importance of proper design, installation, and maintenance of these systems cannot be stressed enough. Failure to pay attention to these details could lead to costly repairs or even the failure of the building envelope. This is why, as an industry professional, you need to be equipped with the best information and expertise, which you will find right here in this ultimate guide. Our guide is structured into five distinct sections, each providing deep insight and practical knowledge:
- Introduction to CSI Division 07 — Thermal and Moisture Protection
- Understanding the Components of Thermal and Moisture Protection
- Selecting Appropriate Materials for Thermal and Moisture Protection
- Techniques for Installing Thermal and Moisture Protection Systems
- Maintenance and Performance Monitoring of Thermal and Moisture Protection Systems
By reading through these sections, you will have a step-by-step understanding of the complexities of thermal and moisture protection systems. You will be able to recognize the various components, identify the best materials to use, master the installation techniques, monitor the systems’ performance, and learn from real-life case studies. So, let’s get started! Join me in this incredible journey through the world of CSI Division 07 — Thermal and Moisture Protection. Let’s master these essential concepts together, and ultimately, help our clients and the industry as a whole achieve higher standards of quality, comfort, and sustainability.
Suggested Posts:
Introduction to CSI MasterFormat and Division 01
Getting to Grips with CSI Division 02 – Existing Conditions in Construction Projects
Mastering Division 09 – Finishes in the CSI MasterFormat System for Improved Project Success
Understanding CSI MasterFormat: Division 14- Conveying Equipment
Master the Art of Utilities Construction with CSI Division 33
Division 48 – A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Power Generation in Construction
Introduction to CSI Division 07 — Thermal and Moisture Protection
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on mastering CSI Division 07 – Thermal and Moisture Protection. Construction projects, whether they are small residential buildings or large commercial structures, require proper thermal and moisture protection systems. These systems not only ensure the comfort, health, and safety of the building’s occupants but also serve as a vital element in the overall structural integrity, energy efficiency, and durability of the building.
In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of proper design, installation, and maintenance of thermal and moisture protection systems. Our goal is to provide you with an easy-to-understand guide that offers a step-by-step understanding of the topic.

What is CSI Division 07?
The Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) has established a classification system called the MasterFormat, which organizes construction-related information into a standardized structure. Division 07 is a part of this system and focuses specifically on thermal and moisture protection. It includes components such as insulation, air and vapor barriers, waterproofing, and roofing, which play a crucial role in protecting the building envelope against the effects of temperature fluctuations and moisture infiltration.
Why is Thermal and Moisture Protection Important?
Without adequate thermal and moisture protection, buildings are susceptible to a wide range of problems, including mold and mildew growth, condensation issues, reduced energy efficiency, and even structural damage. Properly designed and installed systems not only prolong the life of the building but also contribute to improved indoor air quality and comfort for occupants. Furthermore, well-executed thermal and moisture protection can lead to significant energy savings, reducing the building’s overall carbon footprint and environmental impact.
The Role of Construction Specification Experts
By understanding the various components, selecting the right materials, and implementing proper installation and maintenance strategies, you can help ensure the success of your building projects in terms of both performance and sustainability.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the components of thermal and moisture protection, explore material selection and installation techniques, discuss maintenance and performance monitoring, and examine real-life case studies that showcase the best practices in the field. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to tackle the challenges of thermal and moisture protection in your future construction projects.

Understanding the Components of Thermal and Moisture Protection
In this section, we’ll dive deeper into the specific components that make up an effective thermal and moisture protection system. We’ll discuss the roles of insulation, air barriers, vapor retarders, and waterproofing in maintaining this critical aspect of building performance.
Insulation
Insulation is a crucial component of any thermal and moisture protection system. It reduces heat transfer between the inside and outside of a building, thereby helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption. There are various types of insulation, including fiberglass, spray foam, and rigid foam boards, as well as natural materials like cellulose and mineral wool.
Air Barriers
Air barriers serve to control the movement of air in and out of a building, preventing drafts, moisture intrusion, and energy loss. They can be constructed using a variety of materials, such as self-adhering membranes, spray-applied coatings, and rigid foam boards. Air barriers are essential for improving a building’s energy efficiency and preventing moisture-related problems, such as mold growth and condensation issues.
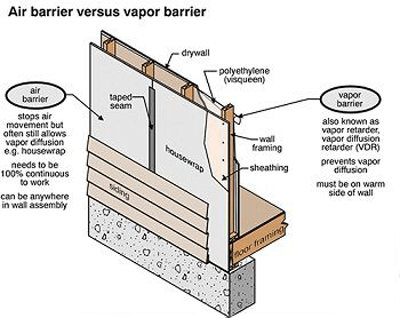
Vapor Retarders
Vapor retarders, also known as vapor barriers, help to limit the amount of moisture that can pass through a building’s walls, floors, and ceilings. These materials, typically made from sheets of plastic, aluminum foil, or other impermeable materials, are critical in preventing condensation, which can lead to structural damage, mold growth, and poor indoor air quality.
Waterproofing
Waterproofing is another essential element of an effective thermal and moisture protection system. It prevents water from infiltrating a building’s foundation, walls, and roofs, protecting the structure from potential water damage, mold, and even corrosion. Waterproofing materials, such as liquid-applied membranes, sheet membranes, and bentonite clay, should be chosen carefully, taking into account factors like the climate, building materials, and project budget.

Applicable Codes and Standards
Several codes and standards govern the design, installation, and maintenance of thermal and moisture protection systems. Some of these include:
- The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) standards, provide guidance on energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and moisture management.
- The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards, establish criteria for evaluating the performance of insulation, air barriers, vapor retarders, and waterproofing materials.
Staying informed about these codes and standards is essential for construction specification experts, as it helps ensure the products and systems they recommend are not only effective but also compliant with industry best practices. In our next section, we’ll explore how to select appropriate materials for thermal and moisture protection, considering factors such as performance, cost, and sustainability. Stay tuned!
Selecting Appropriate Materials for Thermal and Moisture Protection
In this section, we’ll examine the key factors to consider when selecting materials for thermal and moisture protection. We’ll discuss performance criteria, material options, manufacturer recommendations, and how to evaluate and compare products effectively.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Materials
When choosing materials for insulation, air barriers, vapor retarders, and waterproofing, consider the following factors:
- Performance requirements: Ensure the chosen materials meet the performance specifications set by the building codes, industry standards, and project-specific requirements.
- Durability: Opt for materials that have a proven track record of service life and withstand the test of time and environmental factors.
- Cost: Select materials that fit within the project budget but still provide high quality and performance.
- Sustainability: Consider the environmental impact of the materials, including their recyclability and the energy efficiency they provide.
- Compatibility: Ensure the materials are compatible with other building elements and do not cause adverse reactions or deterioration.

Performance Criteria for Insulation, Air Barriers, Vapor Retarders, and Waterproofing
Different materials have varying performance criteria. Evaluate each material based on the following:
- Thermal resistance (R-value): Higher R-value indicates better insulation.
- Air permeance: Lower air permeance indicates better air barrier performance.
- Water vapor permeance: Lower permeance values indicate better vapor retarder performance.
- Waterproofing capabilities: Ability to protect the structure from water intrusion and damage.
Material Options and Their Implications on Project Cost, Durability, and Sustainability
There are numerous material options for thermal and moisture protection, with varying implications for cost, durability, and sustainability:
- Insulation: Fiberglass, mineral wool, spray foam, rigid foam, and cellulose are common insulation materials. Each has its pros and cons, but some are more sustainable (cellulose) or offer better durability (spray foam) than others.
- Air barriers: Common air barrier materials include self-adhered membranes, fluid-applied membranes, and mechanically-attached membranes. Performance varies, and some may be more suitable for specific applications.
- Vapor retarders: Polyethylene sheeting, kraft-faced insulation, and smart vapor retarders are commonly used. Smart vapor retarders offer a higher level of performance and adaptability to interior humidity levels.
- Waterproofing: Waterproofing materials include sheet membranes, fluid-applied membranes, and bentonite clay. Some materials may offer more environmentally friendly options or longer service life.

Manufacturer Recommendations
When selecting materials, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to ensure products are used correctly and in the right applications. These guidelines may also provide information on material compatibility and installation best practices.
Evaluating and Comparing Thermal and Moisture Protection Products
To evaluate and compare different thermal and moisture protection materials, consider:
- Manufacturer specifications, including R-values, air permeance, water vapor permeance, and waterproofing capabilities
- Third-party verification of product performance, such as ASTM or ASHRAE testing
- Reviews and recommendations from other construction specification experts or industry professionals
- Cost-benefit analysis to determine the most appropriate materials for the specific project
By considering these factors and performance criteria when selecting thermal and moisture protection materials, you can make informed decisions that will ultimately contribute to a successful and high-performing construction project.
Techniques for Installing Thermal and Moisture Protection Systems
In this section, we delve into the step-by-step installation procedures for insulation, air barriers, vapor retarders, and waterproofing. By understanding proper installation techniques, construction professionals can ensure long-term performance and avoid common mistakes. Furthermore, we will explore quality control measures and safety considerations when working with these systems.
Insulation Installation
- Select the appropriate insulation material: Choose the insulation material based on factors such as R-value, cost, sustainability, and project-specific requirements.
- Prepare the surface: Clean and dry the area where the insulation will be installed. For wall insulation, install the studs and sheathing before adding the insulation.
- Measure and cut: Measure the insulation to the required size and cut the material using appropriate tools.
- Install the insulation: Insert the insulation between the studs or rafters, making sure it fits snugly without leaving air gaps. For loose-fill insulation, use a blowing machine to distribute the material evenly.
- Seal any gaps: Use foam sealant or other appropriate materials to seal any gaps and ensure continuous insulation.

Air Barrier Installation
- Determine the air barrier location: Choose the right location for the air barrier, considering factors such as climate and building design.
- Select the air barrier material: Common options include self-adhering membranes, fluid-applied barriers, and mechanically fastened wraps.
- Prepare the surface: Clean and dry the substrate, ensuring it is free of defects and contaminants that could compromise the air barrier’s performance.
- Install the air barrier: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for applying the material to the substrate. Ensure the air barrier is continuous and sealed at all seams and penetrations.
- Inspect the installation: Perform a visual inspection and, if required, a blower door test to confirm the air barrier’s effectiveness.

Vapor Retarder Installation
- Determine the vapor retarder location: Consider the building’s climate and design to identify the most appropriate location for the vapor retarder.
- Select the vapor retarder material: Choose the material with the appropriate permeance rating (Class I, II, or III) based on project requirements.
- Install the vapor retarder: Place the vapor retarder on the warm side of the insulation and attach it to the substrate. If multiple layers are required, overlap them to ensure continuity.
- Seal seams and penetrations: Use compatible tapes and sealants to create a continuous barrier and prevent moisture infiltration.

Waterproofing Installation
- Prepare the substrate: Ensure the surface is clean, dry, and free of defects that could impede the waterproofing’s adhesion.
- Select the waterproofing material: Choose the appropriate material based on factors such as exposure, project requirements, and ease of application.
- Apply the waterproofing: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to apply the material to the surface, ensuring a continuous and consistent coverage.
- Inspect the installation: Visually check the waterproofing for potential defects, and if necessary, perform a water immersion or flood test to verify its performance.

Quality Control Measures and Safety Considerations
Regardless of the system being installed, it is crucial to have quality control measures in place, such as regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. Additionally, construction professionals should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow safety protocols when working with thermal and moisture protection systems.
With a thorough understanding of the proper installation techniques for thermal and moisture protection systems, construction professionals can effectively contribute to the overall performance and longevity of their projects. By avoiding common mistakes and ensuring quality control, these systems will effectively protect against cold, heat, and moisture infiltration for years to come.
Maintenance and Performance Monitoring of Thermal and Moisture Protection Systems
Identifying and addressing issues in thermal and moisture protection systems is essential for the long-term performance and durability of a construction project. In this section, we will discuss common signs of system failures, inspection and monitoring methods, maintenance strategies, and the role of construction specification experts in ensuring ongoing performance.
Common Signs of Moisture and Thermal Protection Failures
Thermal and moisture protection systems can fail for various reasons, such as improper installation, material degradation, or damage caused by external factors. Some common signs of system failures include:
- Mold and mildew growth
- Damp or wet spots on walls, ceilings, or floors
- Peeling or blistering paint
- Warped or buckled building materials
- Excessive energy consumption for heating and cooling
- Condensation on windows or doors

It is crucial to address these issues promptly to prevent further damage and potential health hazards for the building occupants.
Inspecting and Monitoring Systems for Signs of Wear or Degradation
Regular inspection and monitoring of thermal and moisture protection systems are essential to detect signs of wear or degradation before they become significant problems. Construction specification experts should develop a comprehensive inspection and monitoring plan, including the following:
- Visual inspections of building envelope components, such as roofing, walls, and windows
- Infrared thermography to identify areas of heat loss or infiltration
- Moisture meters for assessing moisture levels in building materials
- Air pressure tests to measure the effectiveness of air barriers
- Documenting and tracking findings for future reference
Preventive Maintenance Strategies and Scheduling
To ensure long-term performance and durability, construction specification experts should establish a preventive maintenance schedule for thermal and moisture protection systems. Preventive maintenance tasks may include:
- Cleaning and inspecting gutters, downspouts, and drains
- Sealing gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other penetrations
- Inspecting and maintaining insulation, vapor retarders, and air barriers
- Regularly checking and improving the performance of HVAC systems

The frequency of these tasks will depend on the specific materials and systems used in a project, as well as the local climate and environmental conditions.
Addressing Identified Issues: Repair, Retrofit, or Replacement?
When issues are identified during inspection and monitoring, construction specification experts must determine the most appropriate course of action, whether it be repairing the issue, retrofitting the system with new materials or technologies, or replacing the entire system. Factors to consider when making this decision include:
- The extent of the damage or degradation
- The remaining service life of the system
- The cost and feasibility of each option
- Potential impacts on building occupants and operations
Have Questions?
Get in touch with our team to learn more about what Swiftlane can do for you.