Welcome to our comprehensive guide on CSI Division 22 – Plumbing! As a construction specification expert, I understand the complexities and intricacies involved in the design, specification, installation, and maintenance of plumbing systems. This blog post aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of all aspects related to plumbing systems within the context of CSI Division 22.

In today’s construction industry, the importance of standardized construction specifications cannot be overstated. The Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) and the MasterFormat play a crucial role in streamlining and organizing construction project documentation. As part of this system, Division 22 – Plumbing focuses on various elements within the plumbing system, making it a valuable resource for architects, contractors, and suppliers. Throughout this blog post, we will delve into the following sections:
- Introduction to CSI Division 22 – Plumbing
- Plumbing Fixtures and Equipment
- Piping, Valves, and Fittings
- Plumbing System Design and Coordination
- Construction and Installation
From common plumbing fixtures and equipment to specialized ones for commercial and industrial settings, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the materials, features, and installation considerations. We’ll also discuss piping materials, valves, and fittings, essential components that ensure the proper functioning of your plumbing system.
Proper plumbing system design and coordination are vital aspects of any construction project. We will cover the various design phases, the role of plumbing engineers, and the use of building information modeling (BIM) in the design and coordination process. Of course, we can’t forget about construction and installation. We’ll discuss the responsibilities of general contractors and subcontractors, common challenges faced during construction, and tips for effective project management in regard to plumbing installation.
Lastly, we’ll explore the importance of inspection, testing, and maintenance for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your plumbing system. We’ll outline testing methods and standards, as well as the routine and periodic maintenance tasks required to keep your plumbing system in tip-top shape. So, whether you’re an architect, contractor, or property owner looking to learn more about the world of plumbing, this expert guide to CSI Division 22 – Plumbing is the perfect resource for you. Stay tuned as we dive into the depths of plumbing systems, specifications, and best practices!

Suggested Posts:
- Introduction to CSI MasterFormat and Division 01
- Getting to Grips with CSI Division 02 – Existing Conditions in Construction Projects
- Mastering Division 09 – Finishes in the CSI MasterFormat System for Improved Project Success
- Understanding CSI MasterFormat: Division 14- Conveying Equipment
Section 1: Introduction to CSI Division 22 – Plumbing
Welcome to your comprehensive guide to CSI Division 22 – Plumbing! In this blog post, we will explore the world of plumbing through the lens of the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) MasterFormat, the industry’s leading resource for organizing construction project documentation. Our goal is to provide you with valuable insights into the design, specification, and installation of plumbing systems while demonstrating the critical role that Division 22 plays in standardizing and facilitating effective communication between architects, contractors, and suppliers.
Background Information on CSI and the MasterFormat
The CSI is a professional association that aims to improve the construction process by developing and promoting standardized formats for construction documents. The MasterFormat is a comprehensive classification system that covers a wide range of building materials, products, and systems, including plumbing. It provides a consistent structure for organizing and communicating construction information, enabling seamless collaboration between project team members.
Importance of Standardized Construction Specifications
Standardized construction specifications are crucial for ensuring that all project stakeholders adhere to a common set of guidelines and expectations during the construction process. This promotes clear communication, reduces the potential for misinterpretation or errors, and ultimately leads to a more efficient and successful project.
Introduction to Division 22 – Plumbing
Division 22 is a critical component of the MasterFormat, as it encompasses all aspects of plumbing system design, specification, and installation. Plumbing systems are a fundamental element in any building, providing essential services such as water supply, waste disposal, and temperature control. By offering a standardized framework for plumbing documentation, Division 22 helps to ensure that these systems are designed and installed correctly and efficiently.

Overview of the Various Sections within Division 22
Division 22 is subdivided into several sections, each focusing on a specific aspect of plumbing. These sections include:
- 22 00 00 Plumbing
- 22 05 00 Common Work Results for Plumbing
- 22 10 00 Facility Water Distribution
- 22 20 00 Facility Sanitary Sewerage
- 22 30 00 Facility Gas Systems
- 22 40 00 Plumbing Fixtures
- 22 50 00 Pool and Fountain Plumbing Systems
- 22 60 00 Gas and Vacuum Systems for Laboratory and Healthcare Facilities
In the upcoming blog sections, we will delve deeper into the fixtures, equipment, piping, design, construction, and maintenance that comprise the world of Division 22 Plumbing. Stay tuned for a comprehensive exploration of these essential building systems!
Section 2: Plumbing Fixtures and Equipment
Common Plumbing Fixtures and Their Uses
Plumbing fixtures play a crucial role in the distribution and conservation of water in our homes and workplaces. Some of the most common plumbing fixtures include:
- Water closets: Commonly known as toilets, they are used for the disposal of human waste.
- Urinals: Designed for the disposal of liquid waste, typically found in public restrooms.
- Sinks: Used for handwashing, dishwashing, and other cleaning purposes, sinks are available in various materials and styles.
- Faucets: These regulate the flow of water from a plumbing system to a fixture and can be found in different designs and finishes.
- Showers: Used for personal hygiene, showers come in various configurations, including wall-mounted, rainfall, and handheld models.

Specialized Fixtures for Commercial and Industrial Applications
Commercial and industrial settings require specialized plumbing fixtures to cater to their unique needs. Some examples of these fixtures include:
- Grease interceptors: Installed in commercial kitchens, they prevent fats, oils, and grease from entering the public sewer system.
- Emergency eyewash stations: Found in laboratories and industrial facilities, these provide immediate eye flushing in case of chemical contact.
- Floor drains: Common in industries and garages, floor drains help remove excess water and maintain clean and safe working environments.

Plumbing Equipment and Their Roles in the Overall Plumbing System
Plumbing equipment ensures the proper functioning of the overall system. Key components include:
- Water heaters: These appliances provide hot water for domestic and commercial use and come in various types, such as tankless, storage-tank, and solar-powered models.
- Water softeners: Used to treat hard water, water softeners protect plumbing systems and appliances from scale buildup.
- Pumps: These devices ensure efficient water supply and proper drainage in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Material Choices and Considerations for Plumbing Fixtures and Equipment
Selecting the right material for plumbing fixtures and equipment is crucial for durability, performance, and aesthetics. Some popular materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its durability and corrosion resistance, stainless steel is commonly used for sinks, faucets, and commercial plumbing fixtures.
- Ceramic: Widely used for toilets, sinks, and urinals, ceramic is easy to clean, resistant to stains, and maintains an attractive appearance.
- Brass: Often used for faucet components, brass is a strong and durable material that offers corrosion resistance and a visually appealing finish.
When selecting plumbing fixtures and equipment, keep in mind factors like budget, design preferences, and project requirements to make an informed decision. Understanding the various options available within CSI Division 22 will help drive choices that ensure a functional and efficient plumbing system.
Section 3: Piping, Valves, and Fittings
A well-designed plumbing system is only as efficient as the materials used to build it. This section will delve into the various types of piping materials, valves, and fittings that comprise the plumbing systems of modern buildings. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of these components will allow construction professionals to make informed decisions for their projects.
Types of Piping Materials and Their Applications
When selecting piping materials, it’s important to consider the specific needs of each application. Common materials include:
- Copper: Known for its durability, longevity, and resistance to corrosion, copper is often used for water supply and gas lines. It can be utilized for both hot and cold water and is easily soldered, making it a popular choice for many plumbing systems.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is a lightweight, cost-effective option for drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems. Especially well-suited for underground installations, PVC is resistant to most chemicals and offers excellent resistance to wear and tear.
- PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene): Becoming increasingly popular in residential applications, PEX is highly resistant to corrosion, scale build-up, and freezing. Its flexibility allows for easy installation in tight spaces, and it requires less connection points, reducing the chance of leaks.
Valves and Their Role in Controlling and Regulating Water Flow
Valves play an essential role in controlling and regulating water flow within a plumbing system. Common types of valves include:
- Ball valves: Operated by a lever, these valves provide a tight seal and are used for shut-off applications.
- Gate valves: Commonly found on main water shut-off points, these valves provide superior flow control but are not recommended for frequent use due to potential wear-and-tear.
- Pressure-reducing valves: Used to reduce water pressure in the system, these valves protect pipes and fixtures from damage caused by excessive pressure.
- Check valves: Preventing backflow, these valves ensure that water only flows in one direction within the system.
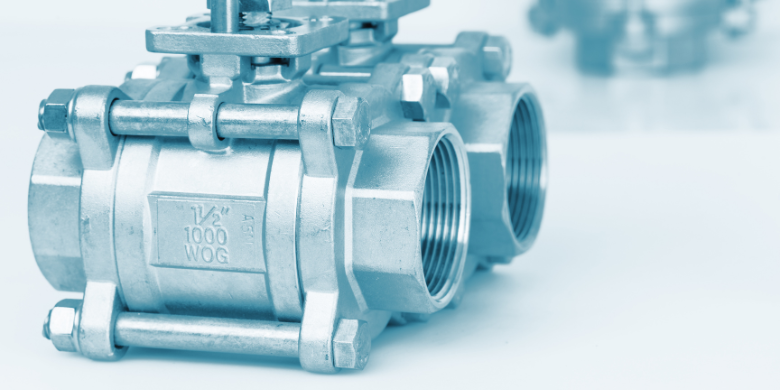
Fittings and Their Use in Connecting and Branching Pipes
Fittings are utilized to connect, branch, or extend pipes within a plumbing system. Common types of fittings include:
- Tees: Allowing for the branching of pipes, tees typically have one inlet and two outlets.
- Elbows: Facilitating changes in direction, elbows come in various angles, such as 45 or 90 degrees.
- Couplings: Used to join two pipes together, couplings can either be rigid or flexible, depending on the application.
- Adapters: Connecting pipes of different materials or sizes, adapters ensure a continuous and leak-free connection.
Proper Installation Techniques and Best Practices for Piping, Valves, and Fittings
To ensure a successful installation and reliable plumbing system, it’s essential to adhere to proper installation techniques and best practices for piping, valves, and fittings. Some key considerations include:
- Thoroughly plan your plumbing system design, taking into account the building’s structure, existing systems, and future needs.
- Choose appropriate materials based on the intended function, local codes and regulations, and environmental factors.
- Properly measure and cut pipes, ensuring they are deburred before connecting.
- Ensure all connections are secure, using appropriate sealants or soldering techniques.
- Install valves and fittings per manufacturer recommendations and test for leaks before putting the system into operation.
Understanding the various components that make up a plumbing system is crucial for construction professionals. By selecting appropriate materials, valves, and fittings, and employing proper installation techniques, you can ensure a long-lasting and efficient plumbing system for your project.
Section 4: Plumbing System Design and Coordination
Designing a plumbing system can be a complex process that requires collaboration among various professionals and coordination with other building systems. In this section, we’ll explore the different stages involved in designing a plumbing system, the importance of teamwork and inter-disciplinary coordination, and the role of modern technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) in enhancing the design process.
4.1 Phases of a Plumbing System Design
The design process begins with schematic design, where the conceptual layout of the plumbing system is developed based on building requirements, code regulations, and preliminary architectural plans. Here, the plumbing engineer considers factors like fixture quantity, fixture types, pipe sizes, and equipment locations to create an initial design outline.
Following the schematic design, the next phase is design development, where the plumbing engineer refines the design, calculates flow rates, reviews material selections, and incorporates more details into the system layout.
The final phase, construction documentation, involves preparing detailed drawings and specifications that clearly communicate the design intent to the contractors responsible for building the system. This crucial stage ensures that the plumbing system is built according to the design and codes, and helps prevent costly changes during construction.
4.2 Collaboration and Coordination Among Design Professionals
Effective communication and collaboration between the plumbing engineer, architect, and other design professionals are critical to a successful project. The plumbing system must be coordinated with various building components like HVAC, electrical, and structural systems. Regular meetings and design reviews are essential to ensure that each discipline’s requirements are addressed and potential conflicts are resolved before construction begins.
4.3 BIM and Digital Design Tools for Plumbing System Design
Modern design tools, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), have revolutionized the way plumbing systems are designed and coordinated. BIM creates a 3D digital representation of the building, which enables design professionals to visualize and simulate the performance of their plumbing systems in a virtual environment. This holistic approach to design improves communication, detects conflicts between systems, and enhances overall project coordination.
4.4 Compliance with Codes and Regulations
During the design process, plumbing engineers must ensure compliance with local and national codes and regulations. These codes outline the minimum requirements for designing and installing plumbing systems, and they aim to ensure public health, safety, and welfare. Plumbing engineers must remain up-to-date with new codes and regulations to provide efficient and compliant plumbing system designs.
In conclusion, the design and coordination of a plumbing system involve a multi-stage process that requires collaboration among various design professionals, efficient use of digital design tools like BIM, and adherence to codes and regulations. By following these best practices, the plumbing system will function effectively, meeting both the building’s needs and code requirements.
Section 5: Construction and Installation
In this section, we dive into the construction and installation phase of a plumbing project, where all the planning and design decisions come to life. Ensuring a smooth and efficient implementation of the plumbing system is essential for the success of the construction project. Thus, it is crucial to understand the responsibilities of the involved parties, anticipate common challenges, and learn strategies for effective project management during plumbing installation.

Roles in Plumbing Installation
The general contractor (GC) is typically responsible for coordinating the overall construction project, from managing subcontractors to ensuring compliance with regulations. They are the primary point of contact for clients and play a crucial role in overseeing project schedules and budgets. The plumbing subcontractor is the specialist responsible for installing the plumbing system as per the specifications outlined in the design documents. Coordinating with the GC and other subcontractors, they ensure the plumbing system is installed efficiently and safely while meeting the project requirements and adhering to codes and regulations.
Importance of Proper Installation Techniques
A well-functioning plumbing system relies heavily on proper installation methods. The quality of the materials and the installation techniques used determines the durability and efficiency of the plumbing system. To avoid future issues like leaks, corrosion, or malfunctions, ensure that the plumbing subcontractor follows approved installation protocols and best practices.
Common Challenges in Plumbing System Construction
In the construction industry, various challenges may arise during the plumbing installation process, such as:
- Scheduling conflicts: Coordinating the work of multiple subcontractors can be challenging. It’s essential to establish an effective project timeline and maintain clear communication between all stakeholders to avoid scheduling conflicts.
- Coordination issues: The plumbing system interacts with other building systems, such as HVAC and electrical. Careful coordination is required to ensure that these systems are integrated seamlessly, avoiding conflicts or delays.
- Material procurement delays: Delays in obtaining necessary materials can bring construction to a halt. Ensure that all materials are ordered promptly, and contingencies are in place in case of supply chain disruptions.
Tips for Effective Project Management in Plumbing Installation
To ensure a smooth plumbing installation process, consider the following tips:
- Clear communication: Establishing effective communication channels between the GC, plumbing subcontractor, and other subcontractors is crucial. Regular meetings and progress updates can help maintain transparency and avoid miscommunications.
- Detailed planning: Thoroughly plan each phase of the plumbing installation, including material procurement, and establish clear roles and responsibilities for each team member.
- Contingency planning: Identify potential risks and develop contingency plans to address them. This involves maintaining a flexible schedule and having alternative suppliers or materials on hand to minimize disruptions.
- Available resources: Familiarize yourself with the local codes, regulations, and permitting requirements to ensure the plumbing system is compliant. Additionally, make use of construction management software and tools for efficient project planning and execution.
In summary, a successful plumbing system construction and installation process relies on effective management, coordination, and communication among all stakeholders. By following best practices, addressing potential challenges, and leveraging available resources, construction professionals can ensure that the installed plumbing system meets the project requirements and provides long-lasting, reliable performance.
Upgrade Your Building Security
Get in touch with a Swiftlane specialist for more information on the best access control and video intercom solution for your building.